May 1, 2023The mechanism of hemostasis can divide into four stages. 1) Constriction of the blood vessel. 2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug.” 3) Activation of the coagulation cascade. 4) Formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot. Purpose.
Life | Free Full-Text | Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines
Step 1: Injured tissue (vessel) releases thromboplastin and collected platelets release platelet factors. Both thromboplastin and platelet factors react with clotting factors in the plasma to produce prothrombin activator.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Primary hemostasis (platelet clotting) Primary hemostasis is when your body forms a temporary plug to seal an injury. To accomplish that, platelets that circulate in your blood stick to the damaged tissue and activate. That activation means they can “recruit” more platelets to form a platelet “plug” to stop blood loss from the damaged area.

Source Image: imrpress.com
Download Image
Intrinsic Pathway of Coagulation and Thrombosis | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Feb 19, 2023There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation (blood clotting). Failure of any of these steps will result in hemorrhage —excessive bleeding. Vascular Spasm When a vessel is severed or punctured, or when the wall of a vessel is damaged, vascular spasm occurs.
Source Image: assaygenie.com
Download Image
Select The Appropriate Pathway For The Steps Of Hemostasis
Feb 19, 2023There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation (blood clotting). Failure of any of these steps will result in hemorrhage —excessive bleeding. Vascular Spasm When a vessel is severed or punctured, or when the wall of a vessel is damaged, vascular spasm occurs. Jan 17, 2023Key Points. Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.It involves three steps: (1) vascular spasm ( vasoconstriction ); (2) platelet plug formation; and (3) coagulation. Vasoconstriction is a reflex in which blood vessels narrow to increase blood pressure. Next, platelet plug formation involves the activation
The Blood Coagulation Pathway and related Disorders – Assay Genie
There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation (blood clotting). Failure of any of these steps will result in hemorrhage —excessive bleeding. Vascular Spasm When a vessel is severed or punctured, or when the wall of a vessel is damaged, vascular spasm occurs. Hemostasis – Part 1 – Primary and Secondary Hemostasis – Med Lab Study Hall

Source Image: medlabstudyhall.com
Download Image
Blood coagulation cascade – products and pathway c … There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation (blood clotting). Failure of any of these steps will result in hemorrhage —excessive bleeding. Vascular Spasm When a vessel is severed or punctured, or when the wall of a vessel is damaged, vascular spasm occurs.

Source Image: abcam.com
Download Image
Life | Free Full-Text | Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines May 1, 2023The mechanism of hemostasis can divide into four stages. 1) Constriction of the blood vessel. 2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug.” 3) Activation of the coagulation cascade. 4) Formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot. Purpose.

Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Intrinsic Pathway of Coagulation and Thrombosis | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology Primary hemostasis (platelet clotting) Primary hemostasis is when your body forms a temporary plug to seal an injury. To accomplish that, platelets that circulate in your blood stick to the damaged tissue and activate. That activation means they can “recruit” more platelets to form a platelet “plug” to stop blood loss from the damaged area.

Source Image: ahajournals.org
Download Image
Schematic of the primary and secondary phases of hemostasis. (A)… | Download Scientific Diagram Platelets are key players in hemostasis, the process by which the body seals a ruptured blood vessel and prevents further loss of blood. Although rupture of larger vessels usually requires medical intervention, hemostasis is quite effective in dealing with small, simple wounds. There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
JCM | Free Full-Text | Pathophysiology of Coagulation and Emerging Roles for Extracellular Vesicles in Coagulation Cascades and Disorders Feb 19, 2023There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation (blood clotting). Failure of any of these steps will result in hemorrhage —excessive bleeding. Vascular Spasm When a vessel is severed or punctured, or when the wall of a vessel is damaged, vascular spasm occurs.
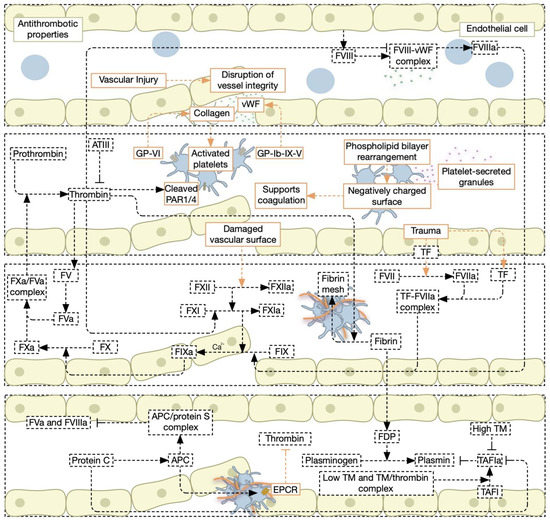
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Secondary Hemostasis Definition and Coagulation Cascade Pathway Steps with Ppt Diagram of Factors — EZmed Jan 17, 2023Key Points. Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.It involves three steps: (1) vascular spasm ( vasoconstriction ); (2) platelet plug formation; and (3) coagulation. Vasoconstriction is a reflex in which blood vessels narrow to increase blood pressure. Next, platelet plug formation involves the activation

Source Image: ezmedlearning.com
Download Image
Blood coagulation cascade – products and pathway c …
Secondary Hemostasis Definition and Coagulation Cascade Pathway Steps with Ppt Diagram of Factors — EZmed Step 1: Injured tissue (vessel) releases thromboplastin and collected platelets release platelet factors. Both thromboplastin and platelet factors react with clotting factors in the plasma to produce prothrombin activator.
Intrinsic Pathway of Coagulation and Thrombosis | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology JCM | Free Full-Text | Pathophysiology of Coagulation and Emerging Roles for Extracellular Vesicles in Coagulation Cascades and Disorders Platelets are key players in hemostasis, the process by which the body seals a ruptured blood vessel and prevents further loss of blood. Although rupture of larger vessels usually requires medical intervention, hemostasis is quite effective in dealing with small, simple wounds. There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, the formation