Kayla_Kuenzer Terms in this set (25) When firms are interdependent, The profit of one firm depends on how its rivals respond to its strategic decisions. The number of firms in an oligopoly must be Small enough so that one firm’s decisions have a significant impact on the decisions of the other firms in the industry.
What Makes a Market an Oligopoly? | St. Louis Fed
• A one firm concentration ratio = (total sales of the largest firm)/(total industry sales) • A eight firm concentration ratio = (total sales of the 8 largest firms)/(total industry sales) A concentration ratio can be defined for any number of firms not just 1, 4, or 8. Notice that concentration ratios must vary between 0 and 1.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Feb 2, 2022Characteristics of an Oligopoly. 1. Interdependence. There are a few interdependent firms that cannot act independently. Firms operating in an oligopoly market with a few competitors must take the potential reaction of its closest rivals into account when making its own decisions. 2. Barriers to Entry.
Source Image: tickertape.in
Download Image
oligopoly | Economics lessons, Teaching economics, Economy lessons Aug 30, 2023A poly oligopoly market refers to a small number of firms producing or consuming the same product. Still, more than two, this type of oligopoly is much more common in reality. The monopolistic competitive market’s number of firms has grown even more. This market type exists between an oligopolistic and a perfectly competitive market.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
The Number Of Firms In An Oligopoly Must Be
Aug 30, 2023A poly oligopoly market refers to a small number of firms producing or consuming the same product. Still, more than two, this type of oligopoly is much more common in reality. The monopolistic competitive market’s number of firms has grown even more. This market type exists between an oligopolistic and a perfectly competitive market. The firm in a monopoly market can set prices and create high barriers for new firms to enter. 2. Oligopoly. An oligopolistic market structure has only a small number of large firms dominated by most market share. Firms in oligopolies need to collude and set a price together. No single firm can change the price by itself.
Microecon – CH 8-9 | PDF | Oligopoly | Profit (Economics)
Expertverified 48. The number of firms in oligopoly industry must be small enough that firms are interdependent in decision making Answer: True A unique feature of an oligopoly type industry is interdependence which means that firms cannot act independently of each … View the full answer Previous question Next question Transcribed image text: What is a Dominant Firm, or a Price Leadership Model? – FreeEconHelp.com, Learning Economics… Solved!

Source Image: freeeconhelp.com
Download Image
Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic Competition – ppt download Expertverified 48. The number of firms in oligopoly industry must be small enough that firms are interdependent in decision making Answer: True A unique feature of an oligopoly type industry is interdependence which means that firms cannot act independently of each … View the full answer Previous question Next question Transcribed image text:

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
What Makes a Market an Oligopoly? | St. Louis Fed Kayla_Kuenzer Terms in this set (25) When firms are interdependent, The profit of one firm depends on how its rivals respond to its strategic decisions. The number of firms in an oligopoly must be Small enough so that one firm’s decisions have a significant impact on the decisions of the other firms in the industry.

Source Image: stlouisfed.org
Download Image
oligopoly | Economics lessons, Teaching economics, Economy lessons Feb 2, 2022Characteristics of an Oligopoly. 1. Interdependence. There are a few interdependent firms that cannot act independently. Firms operating in an oligopoly market with a few competitors must take the potential reaction of its closest rivals into account when making its own decisions. 2. Barriers to Entry.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
SOLVED: As the number of firms in an oligopoly grows large, the industry approaches a level of output that is the competitive level and the monopoly level. a. less than, more than May 10, 2022In this case, profits to each firm are zero, and the oligopoly outcome is the same as that which would have occurred under perfect competition. Demonstration 7.5.3 7.5. 3 reflects the scenario just described and shows why. Suppose that Firm A and Firm B have each chosen the monopoly price of $110. Each makes $2,025.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Market Structure – Monopolisitc Competition and Oligopoly – MARKET STRUCTURE: MONOPOLISTIC – Studocu Aug 30, 2023A poly oligopoly market refers to a small number of firms producing or consuming the same product. Still, more than two, this type of oligopoly is much more common in reality. The monopolistic competitive market’s number of firms has grown even more. This market type exists between an oligopolistic and a perfectly competitive market.
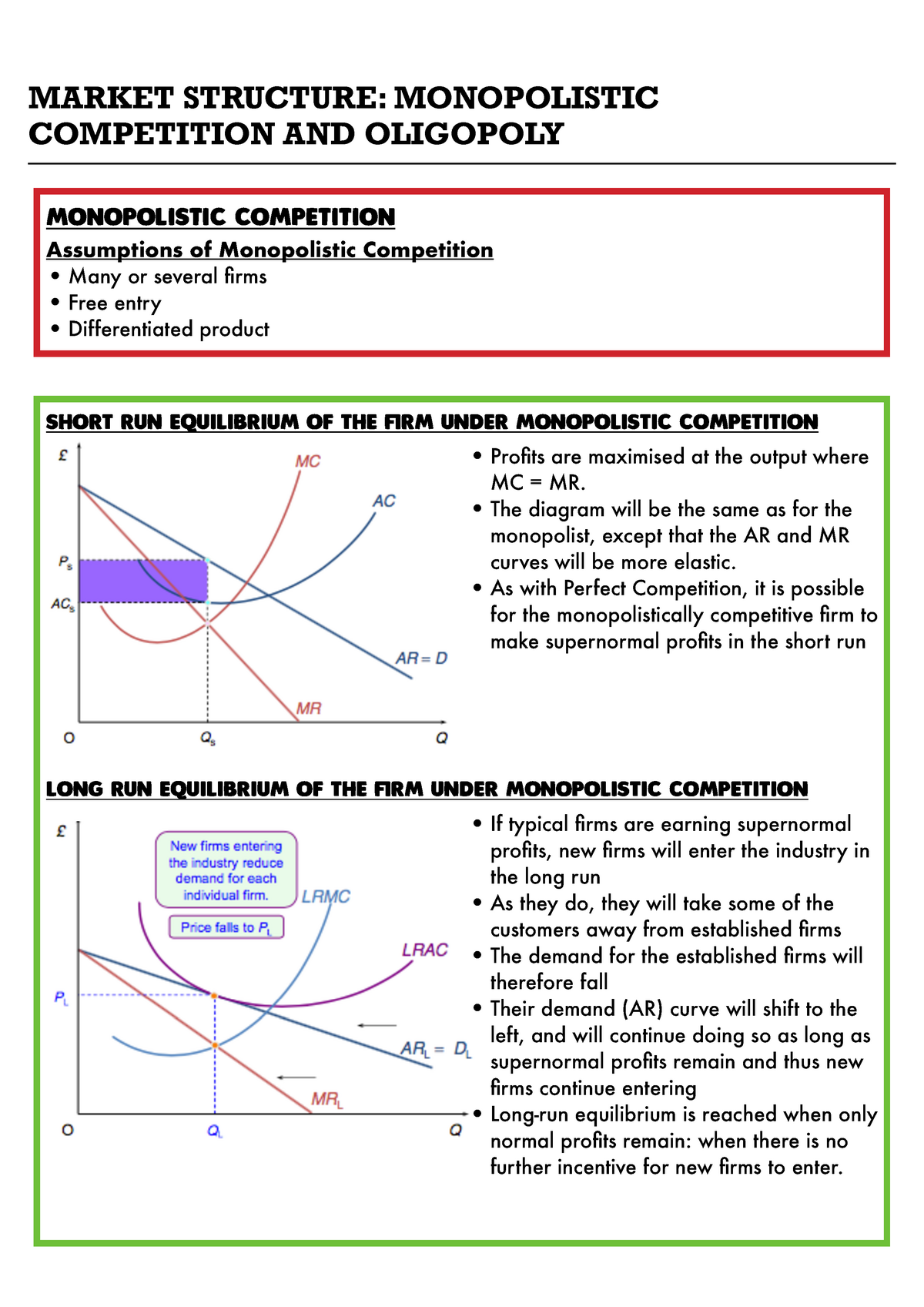
Source Image: studocu.com
Download Image
The number of firms in an oligopolistic industry a. must be less than 10. b. must be less than 20. c. must be small enough that firms are interdependent. d. must be The firm in a monopoly market can set prices and create high barriers for new firms to enter. 2. Oligopoly. An oligopolistic market structure has only a small number of large firms dominated by most market share. Firms in oligopolies need to collude and set a price together. No single firm can change the price by itself.

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Monopoly, Oligopoly, and Monopolistic Competition – ppt download
The number of firms in an oligopolistic industry a. must be less than 10. b. must be less than 20. c. must be small enough that firms are interdependent. d. must be • A one firm concentration ratio = (total sales of the largest firm)/(total industry sales) • A eight firm concentration ratio = (total sales of the 8 largest firms)/(total industry sales) A concentration ratio can be defined for any number of firms not just 1, 4, or 8. Notice that concentration ratios must vary between 0 and 1.
oligopoly | Economics lessons, Teaching economics, Economy lessons Market Structure – Monopolisitc Competition and Oligopoly – MARKET STRUCTURE: MONOPOLISTIC – Studocu May 10, 2022In this case, profits to each firm are zero, and the oligopoly outcome is the same as that which would have occurred under perfect competition. Demonstration 7.5.3 7.5. 3 reflects the scenario just described and shows why. Suppose that Firm A and Firm B have each chosen the monopoly price of $110. Each makes $2,025.