13.4: The Mechanism of Halogenation. Page ID. lkanes (the most basic of all organic compounds) undergo very few reactions. One of these reactions is halogenation, or the substitution of a single hydrogen on the alkane for a single halogen to form a haloalkane. This reaction is very important in organic chemistry because it opens a gateway to
Introduction to Organic Chemistry – Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry (A-Level Chemistry) – Study Mind
Suzuki Reaction 25m. Sonogashira Coupling Reaction 17m. Fukuyama Coupling Reaction 15m. Kumada Coupling Reaction 13m. Negishi Coupling Reaction 16m. Buchwald-Hartwig Amination Reaction 19m. Eglinton Reaction 17m. Learn Free Radical Halogenation with free step-by-step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors.
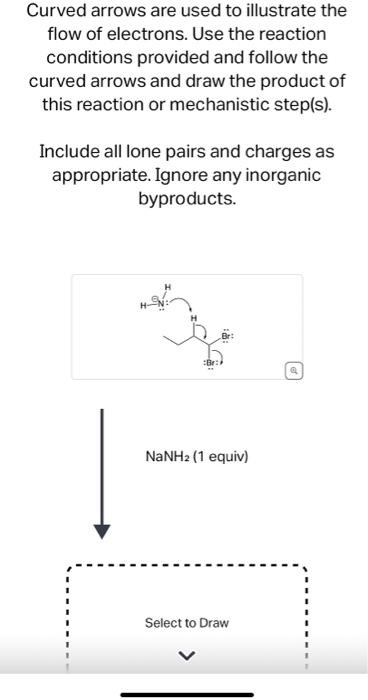
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the halogenation of alkenes. It also covers the halohydrin formation reaction mecha
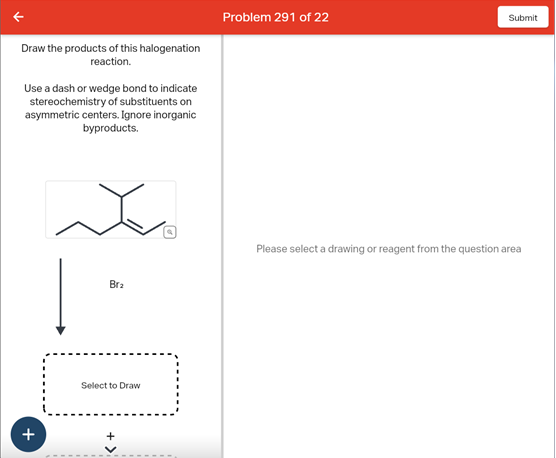
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Solved Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use | Chegg.com
Solvents that are used for this type of electrophilic halogenation are inert (e.g., CCl 4) can be used in this reaction. Because halogen with negative charge can attack any carbon from the opposite side of the cycle it creates a mixture of steric products.Optically inactive starting material produce optically inactive achiral products ( meso
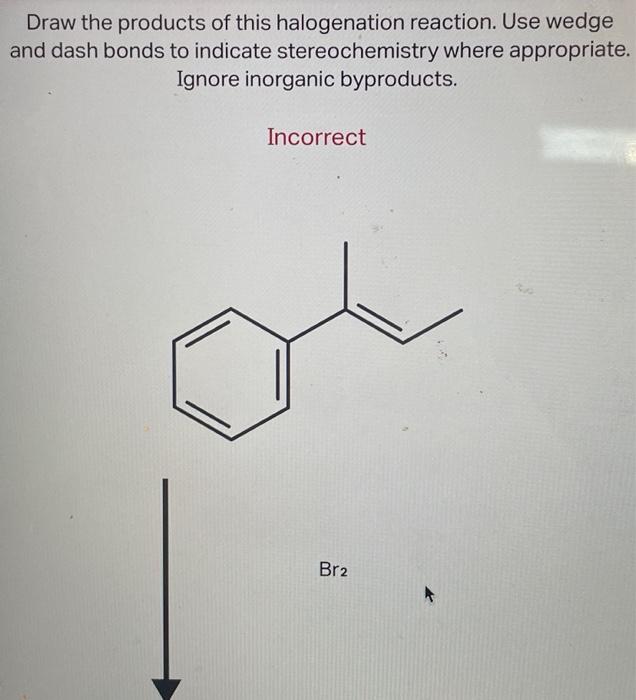
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Draw The Products Of This Halogenation Reaction
Solvents that are used for this type of electrophilic halogenation are inert (e.g., CCl 4) can be used in this reaction. Because halogen with negative charge can attack any carbon from the opposite side of the cycle it creates a mixture of steric products.Optically inactive starting material produce optically inactive achiral products ( meso
Jan 28, 2024Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproducts. Pro Q Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry 2nd Edition ISBN: 9780618974122 Author: Andrei Straumanis Publisher: Andrei Straumanis Chapter10: Oxidation And Reduction
Solved Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use | Chegg.com
Jan 23, 2023Halogenation is the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms in an organic compound by a halogen (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine). Unlike the complex transformations of combustion, the halogenation of an alkane appears to be a simple substitution reaction in which a C-H bond is broken and a new C-X bond is formed.
Solved Draw all of the possible monc hlorinated products | Chegg.com
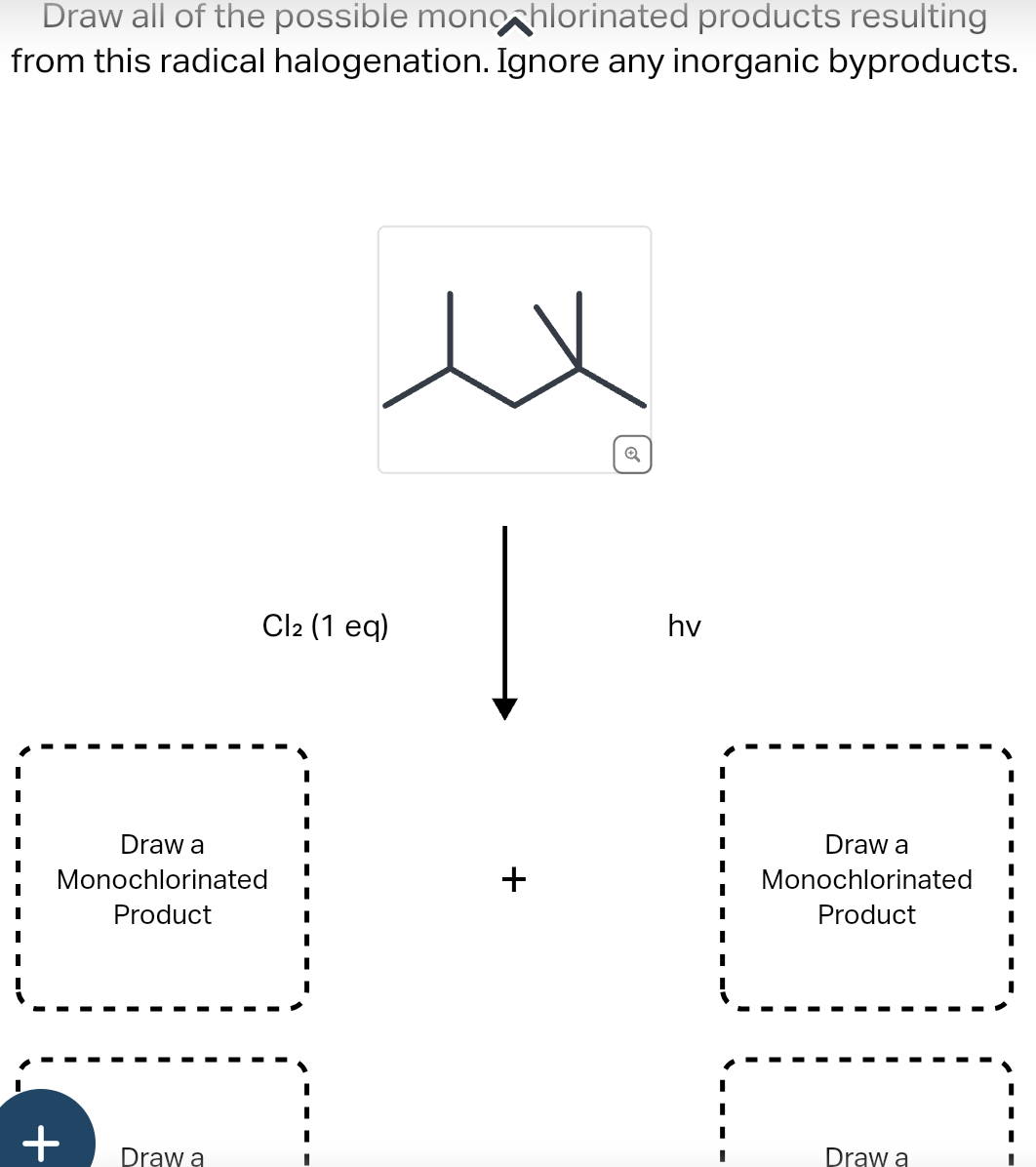
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Answered: Draw the major product of this… | bartleby
Jan 23, 2023Halogenation is the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms in an organic compound by a halogen (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine). Unlike the complex transformations of combustion, the halogenation of an alkane appears to be a simple substitution reaction in which a C-H bond is broken and a new C-X bond is formed.
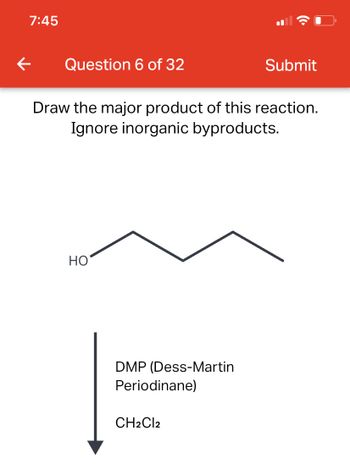
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Introduction to Organic Chemistry – Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry (A-Level Chemistry) – Study Mind
13.4: The Mechanism of Halogenation. Page ID. lkanes (the most basic of all organic compounds) undergo very few reactions. One of these reactions is halogenation, or the substitution of a single hydrogen on the alkane for a single halogen to form a haloalkane. This reaction is very important in organic chemistry because it opens a gateway to
Source Image: studymind.co.uk
Download Image
Solved Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use | Chegg.com
This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the halogenation of alkenes. It also covers the halohydrin formation reaction mecha
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
nucleophilic substitution – How to draw a reaction coordinate diagram for SN1 mechanism? – Chemistry Stack Exchange
What are the products formed in the halogenation reaction given below? [Indicate the stereochemistry of the product and any racemic mixtures.] 6 PRACTICE PROBLEM Identify the missing product (s). 7 PRACTICE PROBLEM Identify the products for the given reaction and indicate the stereoisomers formed, if any. 8 PRACTICE PROBLEM

Source Image: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Download Image
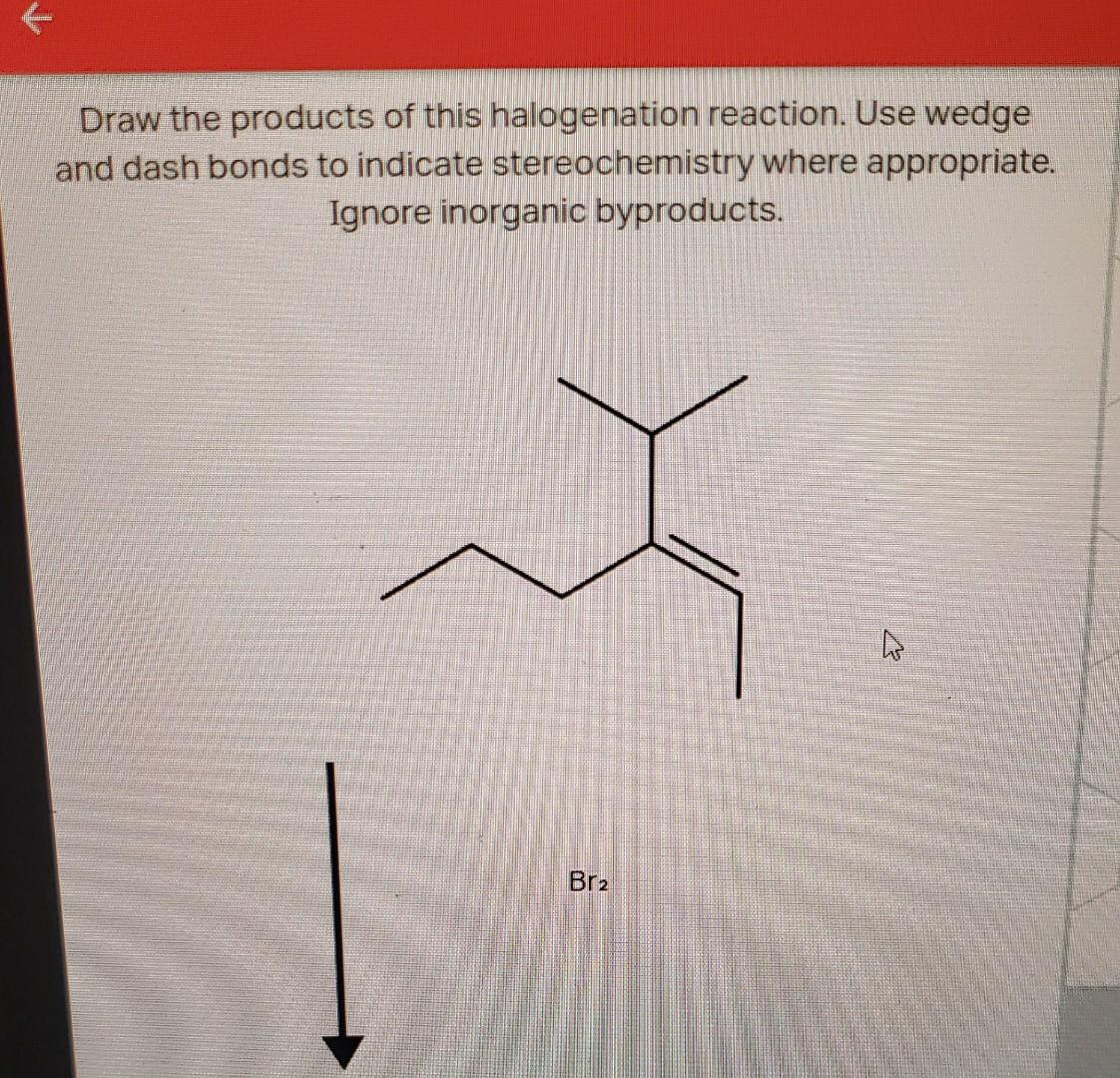
SOLVED: There should be 2 products. Question 12 of 28 Submit Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use wedge and dash bonds to indicate stereochemistry where appropriate. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Br2
Solvents that are used for this type of electrophilic halogenation are inert (e.g., CCl 4) can be used in this reaction. Because halogen with negative charge can attack any carbon from the opposite side of the cycle it creates a mixture of steric products.Optically inactive starting material produce optically inactive achiral products ( meso

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
E2 Reactions — Organic Chemistry Tutor
Jan 28, 2024Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproducts. Pro Q Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry 2nd Edition ISBN: 9780618974122 Author: Andrei Straumanis Publisher: Andrei Straumanis Chapter10: Oxidation And Reduction
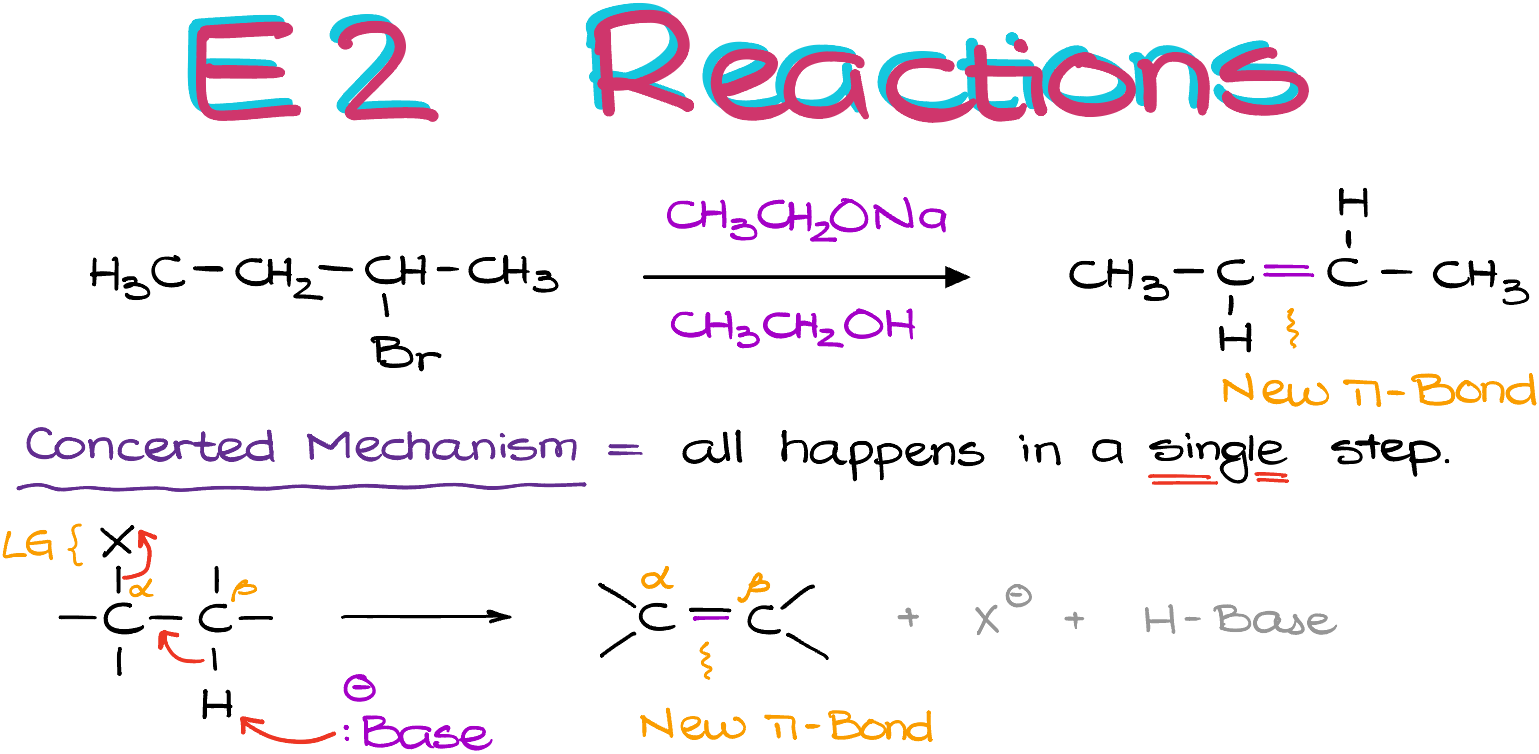
Source Image: organicchemistrytutor.com
Download Image
Answered: Draw the major product of this… | bartleby
E2 Reactions — Organic Chemistry Tutor
Suzuki Reaction 25m. Sonogashira Coupling Reaction 17m. Fukuyama Coupling Reaction 15m. Kumada Coupling Reaction 13m. Negishi Coupling Reaction 16m. Buchwald-Hartwig Amination Reaction 19m. Eglinton Reaction 17m. Learn Free Radical Halogenation with free step-by-step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors.
Solved Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use | Chegg.com SOLVED: There should be 2 products. Question 12 of 28 Submit Draw the products of this halogenation reaction. Use wedge and dash bonds to indicate stereochemistry where appropriate. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Br2
What are the products formed in the halogenation reaction given below? [Indicate the stereochemistry of the product and any racemic mixtures.] 6 PRACTICE PROBLEM Identify the missing product (s). 7 PRACTICE PROBLEM Identify the products for the given reaction and indicate the stereoisomers formed, if any. 8 PRACTICE PROBLEM