Jan 18, 2024First of all, the Charles’ law formula requires the absolute values of temperatures so we have to convert them into Kelvin: T₁ = 35 °C = 308.15 K, T₂ = 15 °C = 288.15 K. Then we can apply the Charles’ law equation in the form where the final volume is being evaluated: V₂ = V₁ / T₁ × T₂. = 2 l / 308.15 K × 288.15 K. = 1.8702 l.
Bulletin Daily Paper 02-14-14 by Western Communications, Inc. – Issuu
A sample of helium has a volume of 521 dm3 at a pressure of 75 cm Hg and a temperature of 18° C. When the temperature is increased to 23° C, what is the volume of the helium? … A 5.00-liter sample of nitrogen gas at 27°C and 320 mm Hg is heated until it occupies a volume of 15.0 liters. If the pressure remains unchanged, the final

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
gas temperature calculator Simply enter the three known measures to calculate the fourth. The calculator uses the combined gas law formula discussed below to perform the computations.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Chemistry Chapter-05 Questions and Answer | PDF | Gases | Combustion A 5.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas?.33 atm. A 10.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas?.66 atm. 4.65 L of nitrogen at standard pressure is compressed into a 0.480 L container. What is the new pressure in kPa?

Source Image: reddit.com
Download Image
A 5.00 L Sample Of Helium Expands To 12.0 L
A 5.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas?.33 atm. A 10.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas?.66 atm. 4.65 L of nitrogen at standard pressure is compressed into a 0.480 L container. What is the new pressure in kPa? A 5.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas? Chemistry. 1 Answer Camilleon May 7, 2018 #P_2# = 33.3 repeating kPa (kilopascals) Explanation: Boyle’s Law #P_1V_1# = #P_2V_2# Standard Temperature and Pressure: 273.15K with an absolute pressure of 1 atm (up to 1982)
A 1.00L gas sample at 100°C and 600 torr contains 50.0% helium and 50.0% xenon by mass. What are the partial pressures of the individual gases? I kind of know how to
Advertisement Expert-Verified Answer question 14 people found it helpful arsilan324 Answer: 1.73 atm Explanation: Given data: Volume = V1 = 5L Volume = V2 = 12.0 L Pressure P2 = 0.720 atm To fnd: Pressure P1 = ? Formula: By using Boyle’s law, P1 x V1 = P2 x V2 Calculation: P1 = (P2 x V2) / V1 = 0.720 atm X 12.0 L / 5L = 8.64/5 = 1.73 atm PPT – Gases Chapter 5 PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:9489400

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
PPT – Chapter 12 Section 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:5757546 Advertisement Expert-Verified Answer question 14 people found it helpful arsilan324 Answer: 1.73 atm Explanation: Given data: Volume = V1 = 5L Volume = V2 = 12.0 L Pressure P2 = 0.720 atm To fnd: Pressure P1 = ? Formula: By using Boyle’s law, P1 x V1 = P2 x V2 Calculation: P1 = (P2 x V2) / V1 = 0.720 atm X 12.0 L / 5L = 8.64/5 = 1.73 atm

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
Bulletin Daily Paper 02-14-14 by Western Communications, Inc. – Issuu Jan 18, 2024First of all, the Charles’ law formula requires the absolute values of temperatures so we have to convert them into Kelvin: T₁ = 35 °C = 308.15 K, T₂ = 15 °C = 288.15 K. Then we can apply the Charles’ law equation in the form where the final volume is being evaluated: V₂ = V₁ / T₁ × T₂. = 2 l / 308.15 K × 288.15 K. = 1.8702 l.

Source Image: issuu.com
Download Image
Chemistry Chapter-05 Questions and Answer | PDF | Gases | Combustion gas temperature calculator Simply enter the three known measures to calculate the fourth. The calculator uses the combined gas law formula discussed below to perform the computations.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
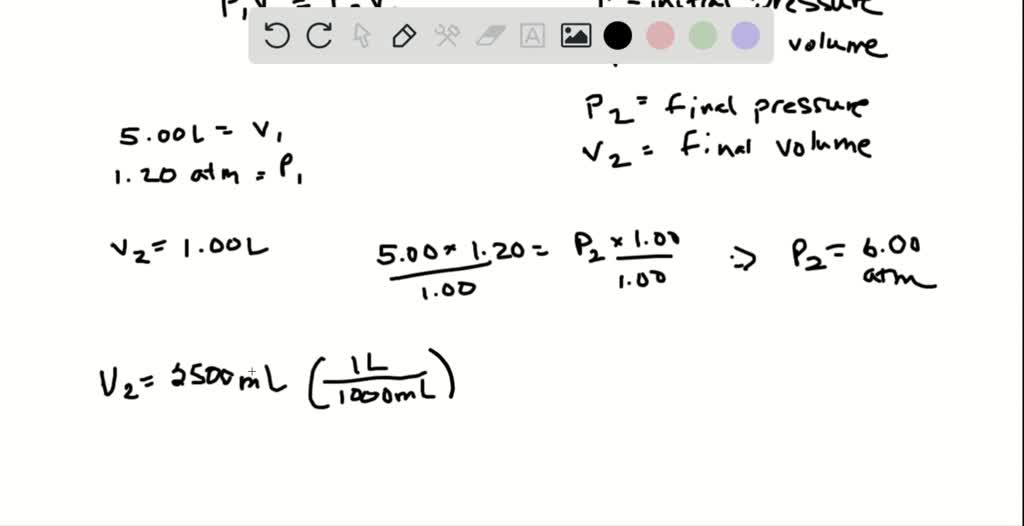
Answered: A 1.20 L weather balloon on the ground… | bartleby Nov 2, 2023Explanation: To solve this problem, we can use Boyle’s Law, which states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional when temperature and amount of gas are constant. Using this formula, we can set up the equation: P1 * V1 = P2 * V2 Plugging in the given values: P1 * 5.00 L = 0.720 atm * 12.0 L Solving for P1:

Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
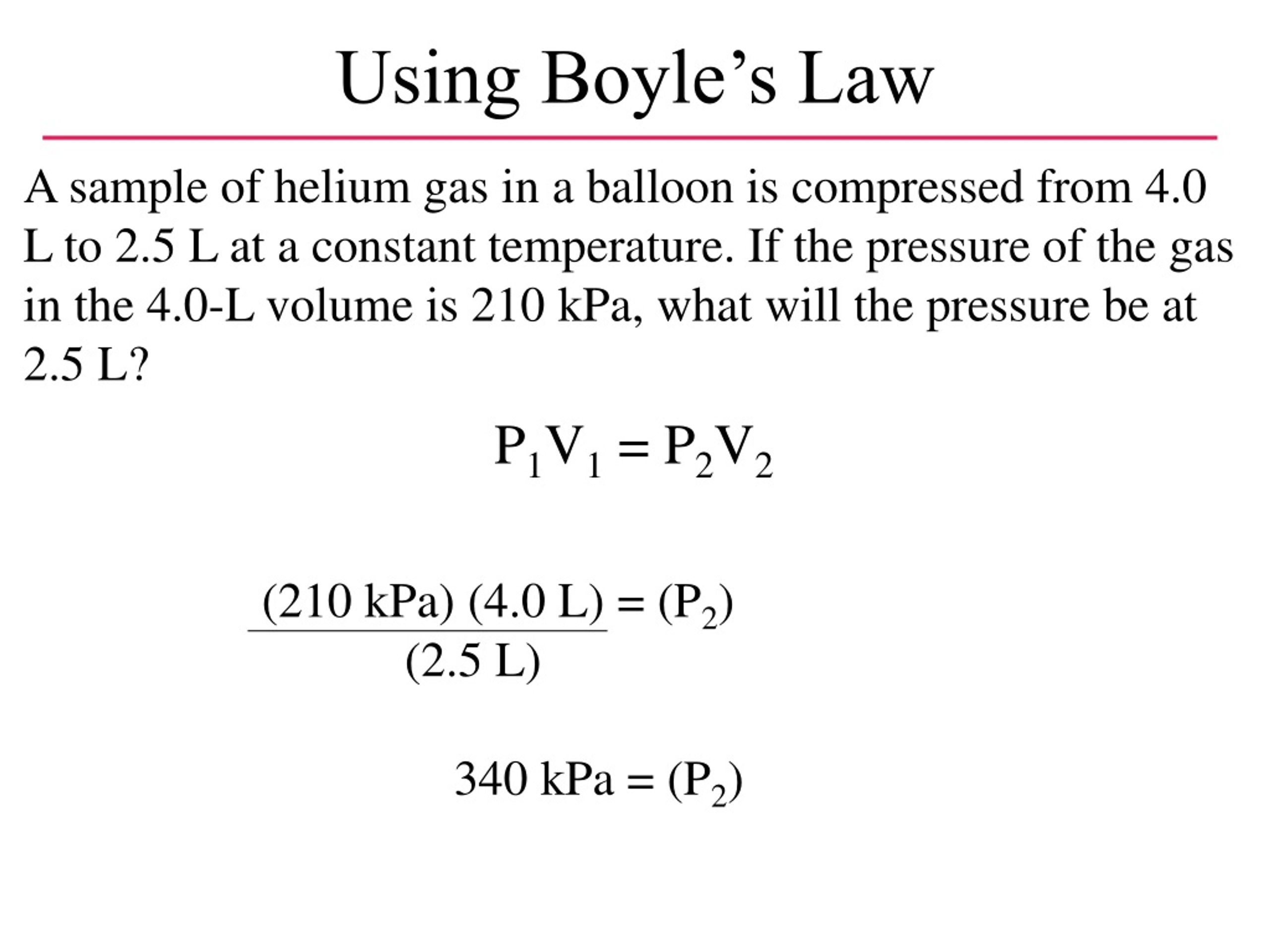
PPT – Chapter 13: Gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:373716 A 5.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas?.33 atm. A 10.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas?.66 atm. 4.65 L of nitrogen at standard pressure is compressed into a 0.480 L container. What is the new pressure in kPa?
Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
d6u htr by darielsoreale – Issuu A 5.00 L sample of helium at STP expands to 15.0 L. What is the new pressure on the gas? Chemistry. 1 Answer Camilleon May 7, 2018 #P_2# = 33.3 repeating kPa (kilopascals) Explanation: Boyle’s Law #P_1V_1# = #P_2V_2# Standard Temperature and Pressure: 273.15K with an absolute pressure of 1 atm (up to 1982)

Source Image: issuu.com
Download Image
PPT – Chapter 12 Section 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:5757546
d6u htr by darielsoreale – Issuu A sample of helium has a volume of 521 dm3 at a pressure of 75 cm Hg and a temperature of 18° C. When the temperature is increased to 23° C, what is the volume of the helium? … A 5.00-liter sample of nitrogen gas at 27°C and 320 mm Hg is heated until it occupies a volume of 15.0 liters. If the pressure remains unchanged, the final
Chemistry Chapter-05 Questions and Answer | PDF | Gases | Combustion PPT – Chapter 13: Gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:373716 Nov 2, 2023Explanation: To solve this problem, we can use Boyle’s Law, which states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional when temperature and amount of gas are constant. Using this formula, we can set up the equation: P1 * V1 = P2 * V2 Plugging in the given values: P1 * 5.00 L = 0.720 atm * 12.0 L Solving for P1: